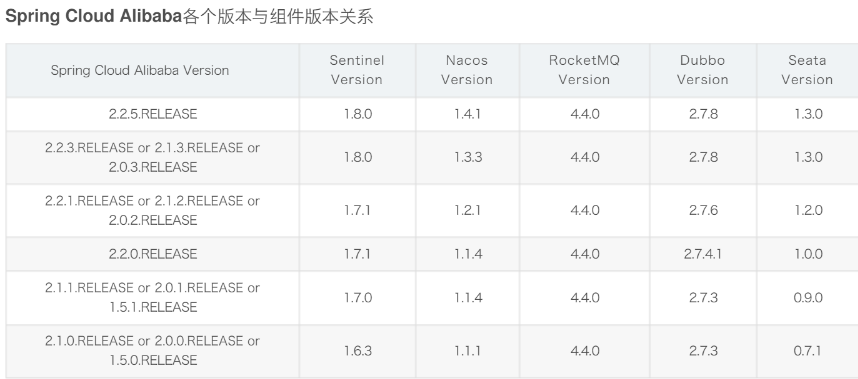
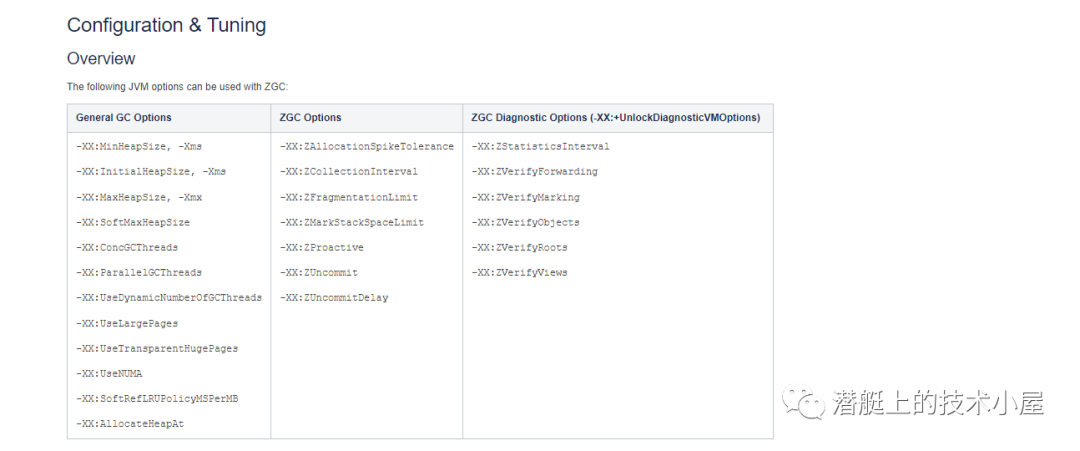
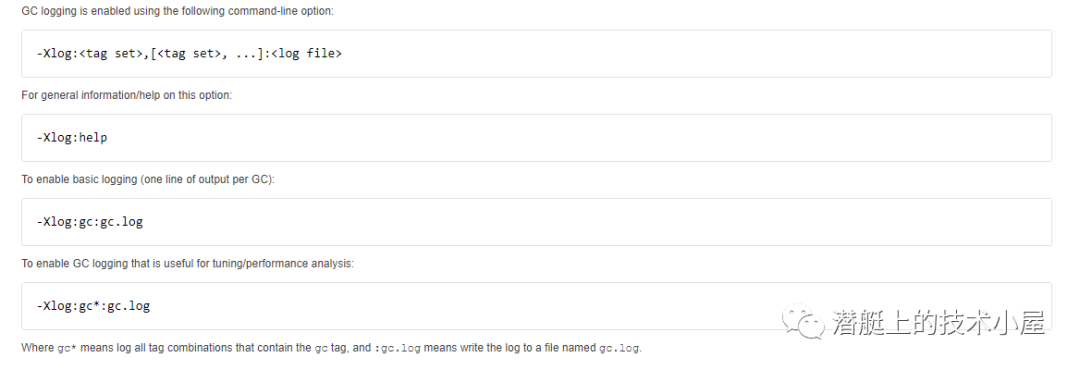
# 【Flutter】Flutter 学习文档
# 前言:如果你要学习 flutter,那么你一定要会 dart 语言,因为 flutter 是基于 dart 来封装的一个 UI 组件包# 本文使用 Typort 书写,禁止转载。# 学习基础要求:# 后端:有语言基础(C/C++/C#/Java/python/Golang 都可以)# 前端 :(JavaScript,Html,CSS) 的人来学习。如果 0 基础,请先学习任意一门后端语言并熟练掌握!# Dart 语言学习: 安装 Dart:https://github.com/GeKorm/dart-windows/releases/download/v1.6.0/Dart_x64.stable.setup.exe
安装好后配置环境变量:DART_HOME E:\dart\bin 安装路径
配置好后 cmd 输入 dart --version 查看环境
1 Dart VM version: 2.3.3-dev.0.0.flutter-b37aa3b036 (Tue Jun 11 13:00:50 2019 +0000) on "windows_x64"
# 注释:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 /* *多行注释 *多行注释 */ /** * 文档注释 与Java相同 */ ///文档注释 dart独有
# 变量定义:dart 语言特点:
自动类型转换,var 声明的变量可以是任意类型!
dart 拥有两种变量定义方式。
指定类型:
String name = “brath”;
或者
类型推导
var name = “brath”; // 推导为任意类型
final name = “brath”; // 不可修改,定义常量,可以初始化
const name = “brath”; // 不可修改,定义常量,不可以初始化,可以被构造修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void main(){ var name = 111111 ; String name1 = "brath用类型定义" ; print ("Hello World! Brath~" ); print (name.runtimeType); print (name1.runtimeType); } console: Hello World! Brath~ int String
# 变量拼接:与 Java 不同,拼接方式用 ${}
如果只拼接普通变量,可以直接 $ 变量名
如果拼接变量引用方法,必须要 $
# 集合类型:list 集合: var names = [“111”,“222”,“333”];
set 集合: var movies = {“111”,“222”,"333”};
map 集合:var info =
默认情况下,dart 的所有 class 都是隐式接口!
# Dart 函数使用:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void main(List<String> args) { print(sum(51 , 14891 )); } int sum(int a,int b){ return a + b; }
# 函数参数:必选参数,不能有默认值,可选参数,可以有默认值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 main(){ sayHello("why" ); } void sayHello(String name){ print (name) } void sayHello2(String name, [int age, String desc]){ sayHello2("brath" ,12 ,"waa" ); } void sayHello3(String name, {int age, String desc}){ sayHello3("brath" ,age: 13 ,desc: "212" ); }
# 函数是一等公民:函数可以作为另外一个函数的参数!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 void main(List <String > args) { test(() => print ("箭头" )); } void test(Function foo){ see(); } void see(){ print ("see!" ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 void main(List <String > args) { var num = demo(); print (num (20 ,12 )); } typedef Calculate = int Function (int num1,int num2);void test(Calculate calculate){ calculate(20 ,30 ); } Calculate demo(){ return (num1,num2){ return num1 * num2; }; }
# 赋值运算符:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Flutter中,有诡异的赋值运算符 比如 name ??="111"; 解释:当原来的变量有值时,不执行 当原来的变量为null时,执行 或者 var name = name ?? "11"; 解释: 当name不为空时使用name,为空使用后面的变量
# 级联运算符:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void main(){ var p = Person() ..name = "brath" ..eat(); ..run(); } class Person () String name; void eat(){ print ("吃" ); } void run(){ print ("跑" ); } }
# For 循环和 Switch 循环与 JS 和 Java 基本一致# 构造函数:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Person{ String name; int age; double height; //默认构造函数 Person(this.name.this.age); //命名构造函数,指定名字的构造函数 Person.NameCon(this.name.this.age,this.height); }
# dynamic:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 dynamic 代表任意类型dynamic obj = "obj" ;print (obj.subString(1 ));Object obj = "obj" ;print (obj.subString(1 ));
# 初始化列表:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 mian(){ var p = Person('brath' ); } class Person final String name; final int age; Person(this .name,{int age}): this .age = age ?? 10 ; }
# 构造函数重定向:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 mian(){ } class Person String name; int age; Person(String name) : this ._internal(name,0 ); Person._internal(this .name,this .age) }
# 工厂构造函数:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Person String name; String color; static final Map <String ,Person> _nameCache = {}; static final Map <String ,Person> _colorCache = {}; factory Person.withName(String name){ if (_nameCache.containsKey(name)){ return _nameCache[name]; }else { _nameCache[name] = Person(name,"default" ); return Person(name,"default" ); } } }
# Getter 和 Setter:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 void main(List <String > args) { final p = Person(); p.name = "brath" ; print (p.name); p.setName("brath.cloud" ); print (p.getName); } class Person late String name; void setName(String name) => this .name = name; String get getName => name; }
# 隐式接口:# 类的混入:1 2 用class 声明的类不可以混入其他类 要混入其他类,使用 mixin 声明该类,并在混入时用with 关键字来连接被混入的类
# 类属性和类方法:1 2 3 4 类属性:在类中不用static 声明的变量,叫做成员变量,不可以被类直接调用 静态属性:在类中用static 声明的变量,叫做静态属性,类属性,可以被类直接调用 类方法:在类中不用static 声明的方法,叫做成员方法,不可以被类直接调用 静态方法:在类中用static 声明的方法,叫做静态方法,类属性,可以被类直接调用
# 枚举的使用:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 void main(List <String > args) { final color = Colors.bule; switch (color){ case Colors.bule: print ("蓝色" ); break ; case Colors.red: print ("红色" ); break ; case Colors.yellow: print ("黄色" ); break ; } print (Colors.values); } enum Colors{ red, bule, yellow }
# 库的使用:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import 'utils/TimeUtil' as timeUtil;show hide import 'utils/TimeUtil' show timeUtil; import 'utils/TimeUtil' hide timeUtil; import 'utils/TimeUtil' show timeUtil, FileUtil; import 'utils/TimeUtil' hide timeUtil, FileUtil;
# 抽取公共库文件:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 以上方法导入库的时候总是会遇到一些问题,比如如果有100 个方法,你只想用50 个,那么你就要用50 个show 或者50 个hide ,但是dart提供了一种方式,就是抽取库到一个公共类中。 前面提到过,dart中所有文件都是一个库,那么我们把需要导入的库,全部export 到一个库中,在引用这个库,就不用担心过多引入了。 公共库: util.dart export 'util/TimeUtil' export 'util/FileUtil' 我的代码: import 'util' ;
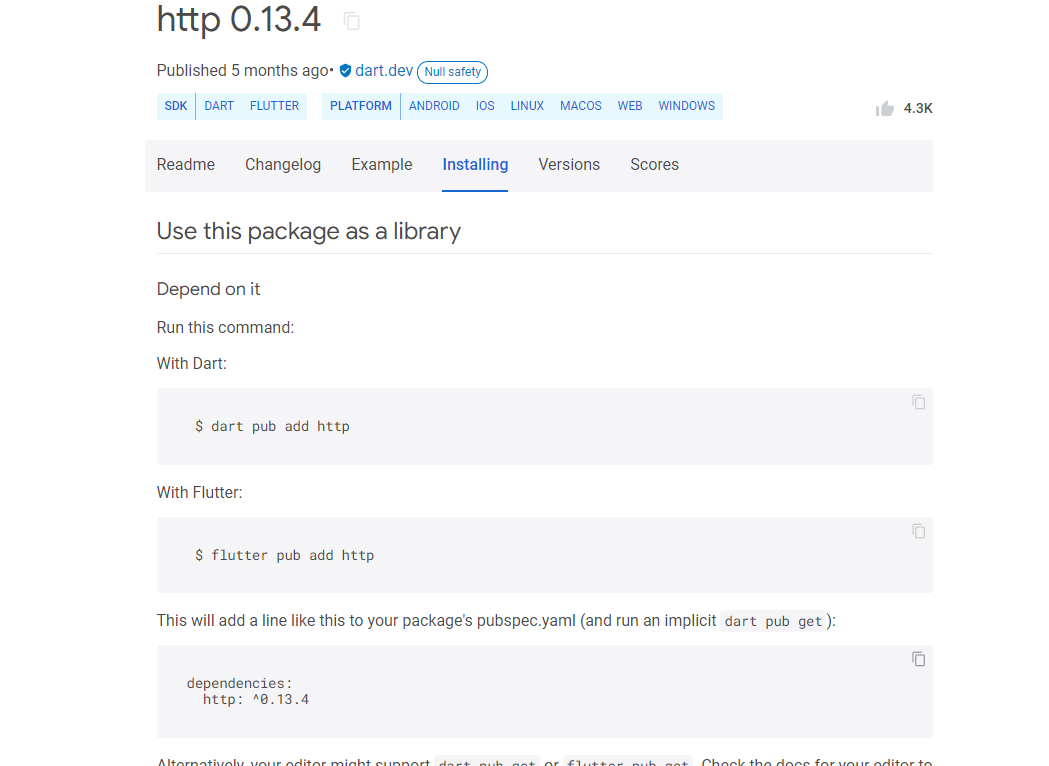
# 使用第三方库:1 2 3 4 5 6 name: 库名 desciption: 描述 dependencies: 依赖 http: ^0.13.4 怎么找库? https://pub.dev/packages/http
点击 installing
把 dependencies 内容复制到代码中
1 2 3 4 5 6 name: coderwhy desciption: a dart dependencies: http: ^0.12.0+4 environment: sdk: '>=2.10.0 < 3.0.0'
进入当前类文件夹,终端输入 pub get 就会下载对应库包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;void main() async { var url = 'https://www.brath.cloud:9000/esn-user-service/user/getUserInfo?id=1' ; var url2 = 'https://brath.cloud/image/back.png' ; var response = await http.get (url); print (response.body); }
# 异常处理: 与 Java 相同但是有不一样的部分:
同步处理
在一个方法中用 try 捕获异常,如果调用方法就捕获不到了!
异步处理
调用一个异步方法如果发生异常,可以用自异步 + await 来捕获异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void main() async { try { await test1(); }catch (e){ print (e); } } test1() async { print (11 ~/0 ); }
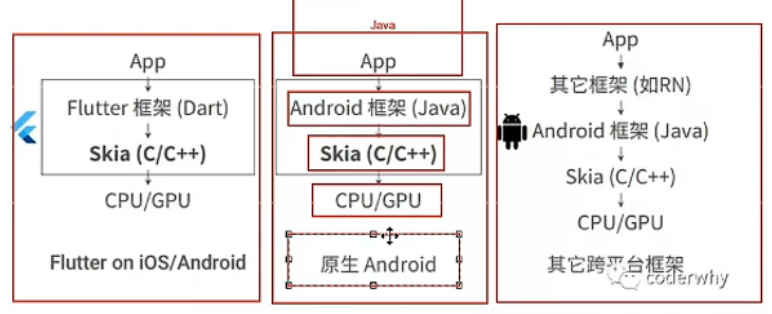
# 接下来介绍 我们的 Flutter!# 最好的跨平台解决方案 Flutter架构对比:
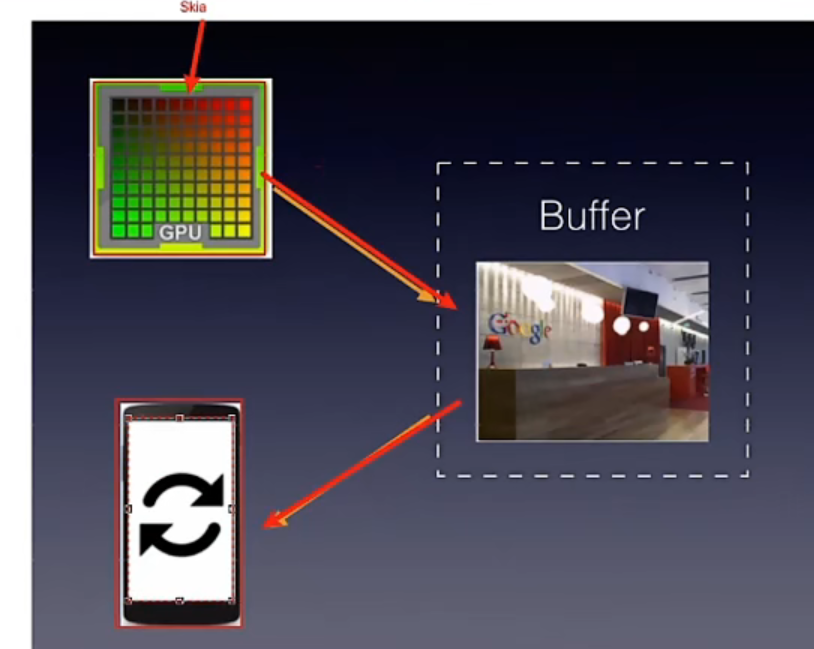
# GUP 绘制出图像,放到 Buffer 缓存中,手机屏幕根据刷新率来读取缓存的操作,就是展示图像。 # 引出了一个概念:垂直同步
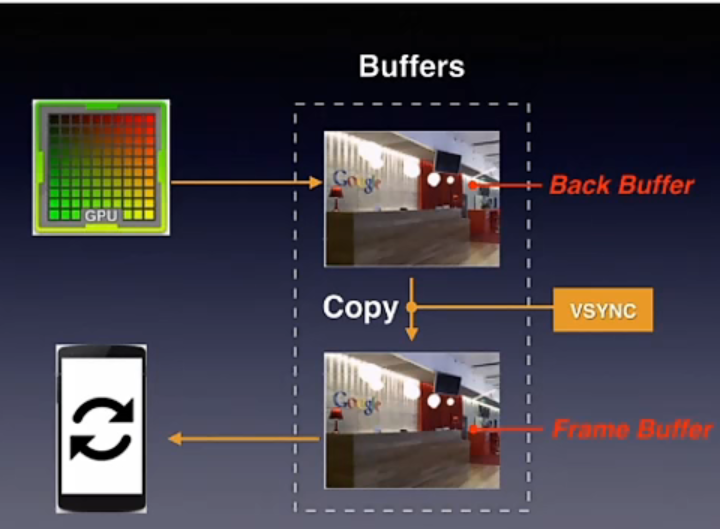
为什么要有垂直同步?
来看一个例子:假设我 GPU 每秒帧率产生 60,手机屏幕每秒也是接受 60,这时可以正常显示。
如果突然每秒帧率提高到 120,手机屏幕可能会来不及读取缓存导致画面重叠、撕裂
开启垂直同后,会有两块缓存区域。
垂直同步就限制了手机屏幕读取缓存和 GPU 产生的速度,开启垂直同步后,GPU 将画面写入到第一个缓存中,第一个缓存会复制内容(地址交换)到第二个缓存中,当两份缓存都存在这一帧,就会发送一个 VSync 的信号,告诉 GPU 可以绘制下一张图,然后手机屏幕来显示第二个缓存中的内容,这样就可以避免图像撕裂。
# 一个简单的 flutter 结构:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import 'package:flutter/material.dart' ;void main() { runApp(const MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( home: BrathScaffoldPage() ); } } class BrathScaffoldPage extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("第一个Fullter程序" ,style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20 ),), ), body: BrathBodyPage() ); } } class BrathBodyPage extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Text("Hello Fullter" ); } }
# 开始学习:# 下载 Flutter SDK配置 Flutter 的第一步就是下载 Flutter SDK,然后进行安装,上面两个地址都有给 SDK 下载地址,这里的问题是有的 SDK 安装包有时会报 没有.git 文件的错误,所以最稳妥的方法是通过 git clone 命令安装
1 git clone -b stable https://github.com/flutter/flutter.git
安装完成之后,可以在安装根目录,找的 flutter_console.bat 文件,双击运行
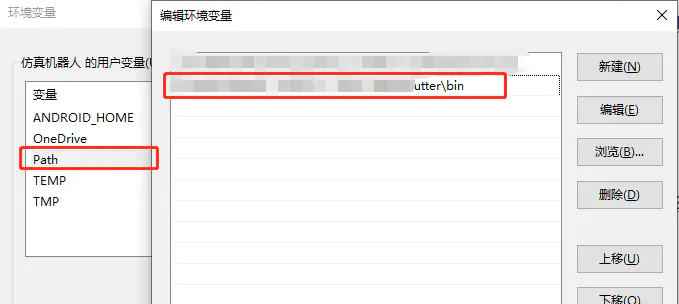
# 配置 Flutter 运行环境变量在用户变量里面编辑或者添加 Path 条目,把 Flutter 的 bin 目录路径添加在里面
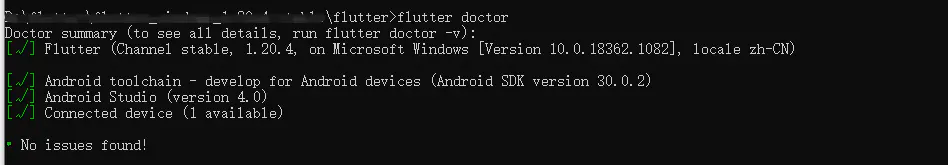
# 运行 Flutter在命令行运行 flutter doctor,它会下载它自己的依赖项并自行编译,一般情况是会报错提示,多半是 Android SDK 找不到什么的,如果出错了,就按照错误信息网上查一下就解决了。
# 编辑器设置我用的 Android Studio,上面连接里面有不同系统和编辑器的流程,详情可以前往查看
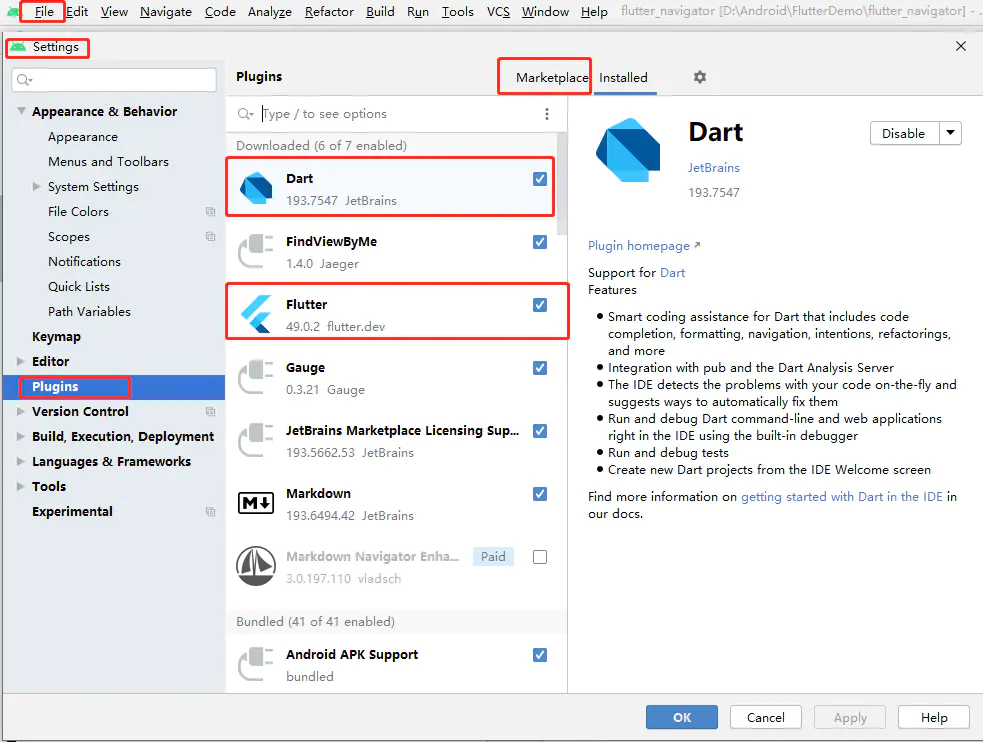
Android Studio 的开发环境就不说了,需要的可以自行百度。Android Studio 配置 Flutter 开发主要是 Flutter 和 Dart 两个插件
File – Settings – Plugins – Marketplace 然后在搜索里面搜索 Flutter 和 Dart 安装就可以了。
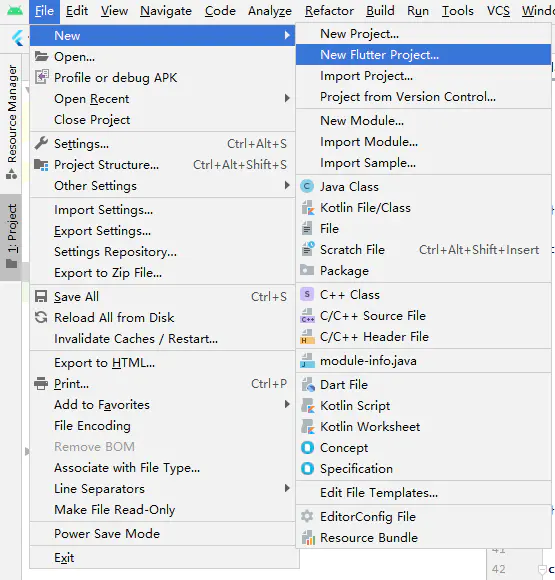
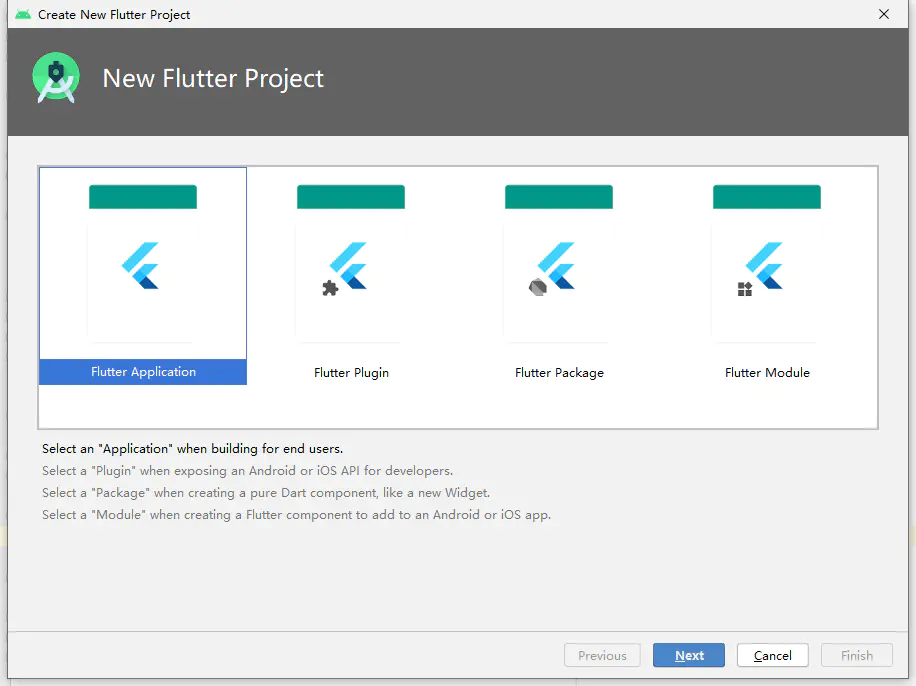
# 新建 Flutter 项目File – New – New Flutter Project
选择 Flutter Application
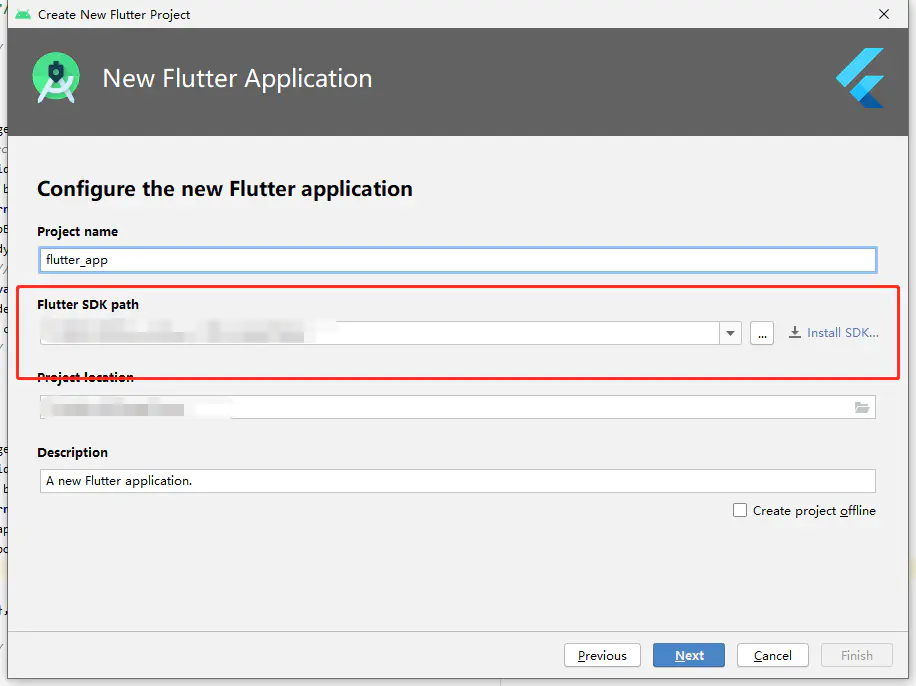
然后到这个最后一步的时候,会有一点小问题
Flutter SDK path 这一栏第一次默认是空的,需要手动选择,选择我们最开始下载的 Flutter SDK,选择根目录,就可以了
# 至此 Flutter 的开发环境安装完毕!# 现在开始学习 Flutter 的基础组件,以及进阶理论!# flutter 学习笔记 auther:Brath# 所有的重点都在代码的注释中标注!# 创建项目: 到想存储项目的文件路径,打开 CMD,输入 flutter create 项目名称即可
vscode 下载好插件,dart 和 flutter 打开对应 flutter 文件,即可开始编写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import 'package:flutter/material.dart' ; main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( ); } }
# 特性:无状态的 widget 是静态页面
有状态的 widget 是动态页面
# 要点:# tips:flutter 的 main 入口调用第一个 widget 需要该 widget 使用 MaterialApp () 作为首个 widget因为 MaterialApp 包含了路由主题等等组件,flutter 规定只能用 MaterialApp 当作根节点
# 使用 MaterialApp 的 home 属性来指定页面1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class MyApp extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false , home: HomePage(), ); } }
均为可选参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Container({ Key? key, this .alignment, this .padding, this .color, this .decoration, this .foregroundDecoration, double? width, double? height, BoxConstraints? constraints, this .margin, this .transform, this .transformAlignment, this .child, this .clipBehavior = Clip.none, }) : assert (margin == null || margin.isNonNegative), assert (padding == null || padding.isNonNegative), assert (decoration == null || decoration.debugAssertIsValid()), assert (constraints == null || constraints.debugAssertIsValid()), assert (clipBehavior != null ), assert (decoration != null || clipBehavior == Clip.none), assert (color == null || decoration == null , 'Cannot provide both a color and a decoration\n' 'To provide both, use "decoration: BoxDecoration(color: color)".' , ), constraints = (width != null || height != null ) ? constraints?.tighten(width: width, height: height) ?? BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: width, height: height) : constraints, super (key: key);
# Text 文本组件 (widget):Text 默认传一个文本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class TextDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build (BuildContext context ) { return Container( width: double .infinity, color: Colors.blue, child: Text( "文本" * 20 , maxLines: 1 , textDirection: TextDirection.ltr, textAlign: TextAlign.center, style: TextStyle( fontSize: 30 , color: Colors.teal ), ) ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 const Text( String this .data, { Key? key, this .style, this .strutStyle, this .textAlign, this .textDirection, this .locale, this .softWrap, this .overflow, this .textScaleFactor, this .maxLines, this .semanticsLabel, this .textWidthBasis, this .textHeightBehavior, }) : assert ( data != null , 'A non-null String must be provided to a Text widget.' , ), textSpan = null , super (key: key);
flutter 中有几种常用按钮组件:
在 2.0 版本后遗弃按钮 RaisedButton 改为 ElevatedButton , FlatButton 改为 TextButton
1 2 RaisedButton 已遗弃 FlatButton 已遗弃
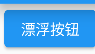
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class ButtonDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed:(){ }, child: Text( "漂浮按钮" ) ) ], ); } }
# TextButton:扁平按钮 / 文本按钮
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class ButtonDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ TextButton( onPressed: (){ }, child: Text( "扁平按钮" )) ], ); } }
# TextButton.icon:带图标的扁平按钮 / 文本按钮
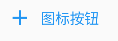
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class ButtonDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ TextButton.icon(onPressed: (){}, icon: Icon(Icons.add), label: Text("图标按钮" )) ], ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class ButtonDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ OutlinedButton(onPressed: (){}, child: Text("无阴影按钮" )) ], ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class ButtonDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ IconButton(onPressed: (){}, icon: Icon(Icons.home)) ], ); } }
flutter 提供了四种图片加载方式:
1、Image.network // 从网络获取图片
2、Image.asset // 从项目本地获取图片
3、Image.file // 从文件路径获取图片
4、Image.memory // 从手机内存,存储中获取图片
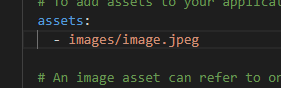
使用 asset 需要设置 pubspec.yaml 中的 assets
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class ImageIconDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ Icon(Icons.home), IconButton(onPressed: (){}, icon: Icon(Icons.home)), Container( width: double .infinity, child: Image.network( "https://brath.cloud/love/GCLK6888.JPG?versionId=CAEQNxiBgID8yJjchBgiIDUzZGFiMWU3YWVlNDQ4YmJhMzMwNDY0Mzk1OGJiOTU1" , fit: BoxFit.fill, ), ), Image.asset("images/image.jpeg" ), ], ); } }
因为开关和复选框是动态的,有状态的,所以我们要使用 StatefulWidget 来做他们的 widget
Check 复选框
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class CheckDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<CheckDemo> createState() => _CheckDemoState(); } class _CheckDemoState extends State <CheckDemo > bool _check = false ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ Checkbox( value: _check, onChanged: (res){ setState(() { _check = res!; }); }), ], ); } }
Switch 开关
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class CheckDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<CheckDemo> createState() => _CheckDemoState(); } class _CheckDemoState extends State <CheckDemo > bool _switch = false ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Column( children: [ Switch( value: _switch , onChanged: (res){ setState(() { _switch = res; }); }) ], ); } }
flutter 为我们提供了几种进度条和指示器样式
1、LinearProgressIndicator 线性指示器
2、CircularProgressIndicator 圆圈指示器
3、CupertinoActivityIndicator IOS 风格的进度指示器
可以设置的参数:
value:可以设置 0 - 1,来表示当前进度
valueColor:使用 AlwaysStoppedAnimation (Colors.red) 动画包裹颜色设置进度指示器的颜色
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class ProgressDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(10 ), child: Column( children: [ LinearProgressIndicator( value: .5 , valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation(Colors.red), ), SizedBox(height: 16 ), Container( height: 100 , width: 100 , child: CircularProgressIndicator( valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation(Colors.red), ), ), SizedBox(height: 16 ), CupertinoActivityIndicator(), ]), ); } }
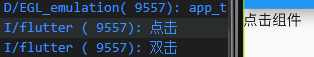
flutter 为我们提供了 GestureDetector 手势检测器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class ClickDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return GestureDetector( onTap: (){ print ("点击" ); }, onDoubleTap: (){ print ("双击" ); }, child: Text("点击组件" ), ); } }
flutter 为我们提供了两种常用输入组件:
TextField:默认典型输入框,没有 validator 验证
TextFromField:特点是可以带参数校验 validator 一般用于登录注册表单验证
# TextField 源码1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 const TextField({ Key? key, this .controller, this .focusNode, this .decoration = const InputDecoration(), TextInputType? keyboardType, this .textInputAction, this .textCapitalization = TextCapitalization.none, this .style, this .strutStyle, this .textAlign = TextAlign.start, this .textAlignVertical, this .textDirection, this .readOnly = false , ToolbarOptions? toolbarOptions, this .showCursor, this .autofocus = false , this .obscuringCharacter = '•' , this .obscureText = false , this .autocorrect = true , SmartDashesType? smartDashesType, SmartQuotesType? smartQuotesType, this .enableSuggestions = true , this .maxLines = 1 , this .minLines, this .expands = false , this .maxLength, @Deprecated ( 'Use maxLengthEnforcement parameter which provides more specific ' 'behavior related to the maxLength limit. ' 'This feature was deprecated after v1.25.0-5.0.pre.' , ) this .maxLengthEnforced = true , this .maxLengthEnforcement, this .onChanged, this .onEditingComplete, this .onSubmitted, this .onAppPrivateCommand, this .inputFormatters, this .enabled, this .cursorWidth = 2.0 , this .cursorHeight, this .cursorRadius, this .cursorColor, this .selectionHeightStyle = ui.BoxHeightStyle.tight, this .selectionWidthStyle = ui.BoxWidthStyle.tight, this .keyboardAppearance, this .scrollPadding = const EdgeInsets.all(20.0 ), this .dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start, this .enableInteractiveSelection = true , this .selectionControls, this .onTap, this .mouseCursor, this .buildCounter, this .scrollController, this .scrollPhysics, this .autofillHints = const <String >[], this .clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge, this .restorationId, this .enableIMEPersonalizedLearning = true , })
# TextFromField 源码1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 Key? key, this .controller, String? initialValue, FocusNode? focusNode, InputDecoration? decoration = const InputDecoration(), TextInputType? keyboardType, TextCapitalization textCapitalization = TextCapitalization.none, TextInputAction? textInputAction, TextStyle? style, StrutStyle? strutStyle, TextDirection? textDirection, TextAlign textAlign = TextAlign.start, TextAlignVertical? textAlignVertical, bool autofocus = false , bool readOnly = false , ToolbarOptions? toolbarOptions, bool? showCursor, String obscuringCharacter = '•' , bool obscureText = false , bool autocorrect = true , SmartDashesType? smartDashesType, SmartQuotesType? smartQuotesType, bool enableSuggestions = true , @Deprecated ( 'Use maxLengthEnforcement parameter which provides more specific ' 'behavior related to the maxLength limit. ' 'This feature was deprecated after v1.25.0-5.0.pre.' , ) bool maxLengthEnforced = true , MaxLengthEnforcement? maxLengthEnforcement, int? maxLines = 1 , int? minLines, bool expands = false , int? maxLength, ValueChanged<String >? onChanged, GestureTapCallback? onTap, VoidCallback? onEditingComplete, ValueChanged<String >? onFieldSubmitted, FormFieldSetter<String >? onSaved, FormFieldValidator<String >? validator, List <TextInputFormatter>? inputFormatters, bool? enabled, double cursorWidth = 2.0 , double? cursorHeight, Radius? cursorRadius, Color? cursorColor, Brightness? keyboardAppearance, EdgeInsets scrollPadding = const EdgeInsets.all(20.0 ), bool enableInteractiveSelection = true , TextSelectionControls? selectionControls, InputCounterWidgetBuilder? buildCounter, ScrollPhysics? scrollPhysics, Iterable <String >? autofillHints, AutovalidateMode? autovalidateMode, ScrollController? scrollController, String? restorationId, bool enableIMEPersonalizedLearning = true , })
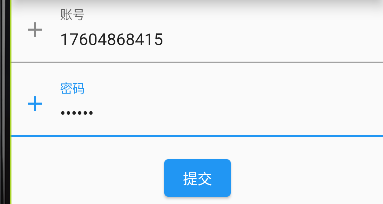
简易登录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class InputDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<InputDemo> createState() => _InputDemoState(); } class _InputDemoState extends State <InputDemo > GlobalKey _key = GlobalKey<FormState>(); TextEditingController _rootController = TextEditingController(); TextEditingController _passController = TextEditingController(); FocusNode _r = FocusNode(); FocusNode _p = FocusNode(); @override void dispose() { super .dispose(); _rootController.dispose(); _passController.dispose(); _r.dispose(); _p.dispose(); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Form( key: _key, child: Column( children: [ TextFormField( autofocus: true , focusNode: _r, controller: _rootController, decoration: InputDecoration( prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.add), labelText: "账号" , hintText: "默认文字" ), validator: (v){ if (v == null || v.isEmpty){ return "账号不能为空!" ; } }, textInputAction: TextInputAction.next, onFieldSubmitted: (v){ print ("brath" ); }, ), SizedBox(height: 8 ), TextFormField( focusNode: _p, controller: _passController, decoration: InputDecoration( prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.add), labelText: "密码" , hintText: "输入密码" ), obscureText: true , validator: (v){ if (v == null || v.length < 5 ){ return "密码不能小于5位数!" ; } }, textInputAction: TextInputAction.send, ), SizedBox(height: 16 ), ElevatedButton( onPressed: (){ print ((_key.currentState as FormState).validate().toString()); }, child: Text("提交" ), ), ]), ); } }
# Flutter 路由工具:var res = await Navigator.of (context).push ( // 跳转路由到 MenuPage 并可以接受返回值
这段代码用异步来监听返回值,优点是,无论是否点击按钮返回,都可以接收到返回值
还可以用 .then ((value) => print (value)); 的方式来获取,这样更简洁,只有返回的时候才会监听,不返回不监听
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 import 'package:flutter/material.dart' ; class LoginPage extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("登录" ), elevation: 10.0 , centerTitle: true , ), body: ElevatedButton( onPressed: () async { var res = await Navigator.of(context).push( MaterialPageRoute( builder: (context) { return MenuPage( menuTitle: "菜单" , ); }, settings: RouteSettings( name: "参数" , arguments: "我是参数" , ), maintainState: false , fullscreenDialog: true , )); print (res); }, child: Text("登录" ), ), ); } } class MenuPage extends StatelessWidget final String menuTitle; const MenuPage({Key? key,required this .menuTitle}) : super (key: key); @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { dynamic arguments = ModalRoute.of(context)?.settings.arguments; return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text(menuTitle + " " + arguments), ), body: ElevatedButton( onPressed: (){ Navigator.of(context).pop("Brath" ); }, child: Text("返回按钮" ), ), ); } }
Flutter 中管理多个页面时有两个核心概念和类: Route 和 Navigator 。route 是一个屏幕或页面的抽象, Navigator 是管理 route 的 Widget 。 Navigator 可以通过 route 入栈和出栈来实现页面之间的跳转。
# 静态路由 (即命名路由)静态路由在通过 Navigator 跳转之前,需要在 MaterialApp 组件内显式声明路由的名称,而一旦声明,路由的跳转方式就固定了。通过在 MaterialApp 内的 routes 属性进行显式声明路由的定义。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build (BuildContext context ) { return MaterialApp ( initialRoute : "/" , routes : { "A" :(context ) => Apage (), "B" :(context ) => Bpage (), "C" :(context ) => Cpage (), }, ); } } 注意:如果指定了home属性,routes表则不能再包含此属性。 如上代码中【home : RootPage ()】 和 【"/" :(context ) => RootPage ()】两则不能同时存在。
例如: RootPage 跳转 Apage 即: RootPage —> Apage
1 Navigator.of(context).pushNamed("A" );
一般方法中带有 Name 多数是通过静态路由完成跳转的,如 pushNamed 、 pushReplacementNamed 、 pushNamedAndRemoveUntil 等。
# 动态路由动态路由无需在 MaterialApp 内的 routes 中注册即可直接使用:RootPage —> Apage
1 2 3 Navigator .of (context).push (MaterialPageRoute ( builder : (context ) => Apage (), ));
动态路由中,需要传入一个 Route , 这里使用的是 MaterialPageRoute ,它可以使用和平台风格一致的路由切换动画,在 iOS 上左右滑动切换,Android 上会上下滑动切换。也可以使用 CupertinoPageRoute 实现全平台的左右滑动切换。PageRouteBuilder : 使用 FadeTransition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Navigator.of(context).push( PageRouteBuilder( transitionDuration: Duration (milliseconds: 250 ), pageBuilder: (BuildContext context,Animation animation, Animation secondaryAnimation){ return FadeTransition( opacity: animation, child: Apage() ); } ) );
到现在为止,可能对路由有了一定的认识,,下面就结合具体方法来详细说明。Navigator.of(context).push 和 Navigator.push 两着并没有特别的区别,看源码也得知,后者其实就是调用了前者。of :获取 Navigator 当前已经实例的状态。
# 路由拦截:flutter 提供了 onGenerateRoute 来使用路由拦截器,作用于强制登录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class MyApp extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false , initialRoute: "/" , routes: { "/" :(context) => LoginPage(), }, onGenerateRoute: (RouteSettings s){ print (s.name); if (s.name != "menu" ){ return MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context){ return LoginPage(); },settings: s); } switch (s.name){ case "menu" : return MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context){ return MenuPage(); },settings: s); break ; } }, ); } }
# 路由方法解释:# pop返回当前路由栈的上一个界面。Navigator.pop(context);
# push / pushNamed :见上,两者运行效果相同,只是调用不同,都是将一个 page 压入路由栈中。直白点就是 push 是把界面直接放入, pushNames 是通过路由名的方式,通过 router 使界面进入对应的栈中。page 。
# pushReplacement / pushReplacementNamed / popAndPushNamed替换路由,顾名思义替换当前的路由。
Replacement.png
由图可知在 BPage 使用替换跳转到 Cpage 的时候, Bpage 被 Cpage 替换了在堆栈中的位置而移除栈, CPage 默认返回的是 APage 。
# pushReplacement 使用的动态路由方式跳转:1 2 3 Navigator .of (context).pushReplacement (MaterialPageRoute ( builder : (context ) => Cpage (), ));
# pushReplacementNamed 使用的静态路由方式,1 Navigator.of(context).pushReplacementNamed("/C" );
两者运行效果相同。
# popAndPushNamed:1 Navigator.of(context).popAndPushNamed("/C" );
其实和上面两个方法运行的结果也是一致,区别就是动画效果不一样: BPage —> CPage 的时候, CPage 会同时有 pop 的转场效果和从 BPage 页 push 的转场效果。简单来说就是 CPage 先 pop 到 BPage ,在 push 到 CPage 。(不知道是不是卡顿的原因,笔者看起来区别不大)
综上:3 中方法结果一样,只是调用方式和过渡动画的区别,开发者自行选择。
# pushAndRemoveUntil / pushNamedAndRemoveUntil在使用上述方式跳转时,会按次序移除其他的路由,直到遇到被标记的路由( predicate 函数返回了 true )时停止。若 没有标记的路由,则移除全部。
# 第一种1 2 3 Navigator .pushAndRemoveUntil (context, MaterialPageRoute (builder : (_ ) => CPage ()), (Route router ) => router == null );
或
1 2 Navigator .of (context).pushNamedAndRemoveUntil ("/C" , (Route router ) => router == null );
此时的路由栈示意图:
RemoveUntil_all.png
可知出了要 push 的 CPage ,当前路由栈中所有的路由都被移除, CPage 变成根路由。
# 第二种:移除到 RootPage 停止1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Navigator .pushAndRemoveUntil (context, MaterialPageRoute (builder : (_ ) => CPage ()), ModalRoute .withName ('/' )) 或 Navigator .pushAndRemoveUntil (context, MaterialPageRoute (builder : (_ ) => CPage ()), (Route router ) => router.settings .name == "/" );
或
1 2 3 Navigator .of (context).pushNamedAndRemoveUntil ("/C" , (Route router ) => router.settings .name == "/" );或 Navigator .of (context).pushNamedAndRemoveUntil ("/C" , ModalRoute .withName ("/" ));
此时的路由栈示意图:
RemoveUntil_until.png
push 到 CPage 的时候,移除到 RootPage 停止, CPage 默认返回 RootPage 。
# popUntil返回到指定的标记路由,若标记的路由为 null ,则程序退出,慎用!!!Replacemen t 和 RemoveUntil 来替换、移除路由了。
until.png
1 2 3 Navigator .of (context).popUntil ((route ) => route.settings .name == "/" );或 Navigator .of (context).popUntil (ModalRoute .withName ("/" ));
再例如:
要实现上述功能,从 CPage 返回到 APage ,并且不在 MaterialApp 内的 routes 属性进行显式声明路由。因为笔者觉得一个应用程序的界面太多了,如果每个界面都要显示声明路由,实在是不优雅。APage ,还是需要标记路由,所有我们在之前跳转 APage 的时候设置 RouteSettings ,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 Navigator .of (context).push (MaterialPageRoute ( settings : RouteSettings (name :"/A" ), builder : (context ) => APage (), ));
在 CPage 需要返回的时候,调用就行:
1 Navigator.of(context).popUntil(ModalRoute.withName("/A" ));
这样代码看起来很优雅,不会冗余。
1 2 Navigator .of (context).popUntil ((route ) => route.isFirst );
# canPop用来判断是否可以导航到新页面,返回的 bool 类型,一般是在设备带返回的物理按键时需要判断是否可以 pop 。
# maybePop可以理解为 canPop 的升级, maybePop 会自动判断。如果当前的路由可以 pop ,则执行当前路由的 pop 操作,否则将不执行。
# removeRoute/removeRouteBelow删除路由,同时执行 Route.dispose 操作,无过渡动画,正在进行的手势也会被取消。
# removeRoute
removeRoute.png
BPage 被移除了当前的路由栈。removeRoute ,则类似于调用 pop 方法,区别就是无过渡动画,所以 removeRoute 也可以用来返回上一页。
# removeRouteBelow移除指定路由底层的临近的一个路由,并且对应路由不存在的时候会报错。
综上:这个两个方法一般情况下很少用,而且必须要持有对应的要移除的路由。
# 路由传值常见的路由传值分为两个方面:
要注意的是,我们一般说静态路由不能传值,并不是说一定不能用于传值,而是因为静态路由一般需要在 MaterialApp 内的 routes 属性进行显式声明,在这里使用构造函数传值无实际意义。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 MaterialApp ( initialRoute : "/" , routes : { "/" :(context ) => RootPage (), "/A" :(context ) => APage ("title" ), "/B" :(context ) => BPage (), "/C" :(context ) => CPage (), }, );
# 向下级路由传值# 1、构造函数传值首先构造一个可以带参数的构造函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 class APage extends StatefulWidget String title; APage(this .title); @override _APageState createState() => _APageState(); }
在路由跳转的时候传值:
1 2 3 Navigator .of (context).push (MaterialPageRoute ( builder : (context ) => APage ("这是传入的参数" ), ));
在 APage 拿到传入的值:
1 2 3 4 Container ( child: Text (widget.title), )
# 2、ModalRoute 传值在 Navigator.of(context).push 的跳转方式中, MaterialPageRoute 的构造参数中 可以看到有 RouteSettings 的属性, RouteSettings 就是当前路由的基本信息
1 2 3 4 5 const RouteSettings({ this .name, this .isInitialRoute = false , this .arguments, });
路由跳转时设置传递参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 Navigator .of (context).push (MaterialPageRoute ( settings : RouteSettings (name :"/A" ,arguments : {"argms" :"这是传入A的参数" }), builder : (context ) => APage (), )); 或使用静态路由pushName: Navigator .of (context).pushNamed ("/A" ,arguments :{"argms" :"这是传入A的参数" });
在 APage 中取值:
1 2 Map argms = ModalRoute.of(context).settings.arguments;print (argms["argms" ]);
# 返回上级路由时传值就是在调用 APage 中调用 pop 返回路由的时候传参
1 Navigator.of (context).pop ("这是pop返回的参数值");
在上一级路由获取:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Navigator.of(context).push(MaterialPageRoute( builder: (context) => APage(), )).then((value ){ print(value ); }); 或 String value = await Navigator.of(context).pushNamed('/xxx' );
1 2 3 4 textDirection: TextDirection.ltr, mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max, mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly, crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
# Column - 纵向概念:纵轴的宽度,默认使用子组件最大宽度
此时,红色和黄色容器宽度为 100 绿色为 150,整个容器就会使用 最大的子组件宽度 150 来表示自己
Column 代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class LayoutDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("布局练习" ), ), body: Container( color: Colors.grey, child: Column(children: [ Container( width: 100 , height: 100 , color: Colors.red, ), Container( width: 150 , height: 100 , color: Colors.green, ), Container( width: 100 , height: 100 , color: Colors.yellow, ), ]), ) ); } }
# Row - 横向概念:和 Colunm 相似,纵轴的宽度,默认使用子组件最大高度
此时,红色和黄色容器高度为 100 绿色为 200,整个容器就会使用 最大的子组件高度 200 来表示自己
Row 代码演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class LayoutDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("布局练习" ), ), body: Container( color: Colors.grey, child: Row( textDirection: TextDirection.ltr, mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max, mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly, crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start, children: [ Container( width: 100 , height: 200 , color: Colors.red, ), Container( width: 150 , height: 100 , color: Colors.green, ), Container( width: 100 , height: 100 , color: Colors.yellow, ), ]), ) ); } }
# Flutter 弹性布局 (Flex):flutter 为我们提供了 Flex 这个 widget 来制造弹性布局
Flex 默认 必传方向 Axis
children 使用 Expanded 来包裹,可以设置 flex 权重,根据数字大小来设置权重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class LayoutDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("布局练习" ), ), body: Container( color: Colors.grey, child: Flex( direction: Axis.vertical, children: [ Expanded(child: Container( width: 100 , height: 200 , color: Colors.red, ),flex: 2 ,), Expanded(child: Container( width: 100 , height: 200 , color: Colors.green, ),flex: 2 ,), Expanded(child: Container( width: 100 , height: 200 , color: Colors.yellow, ),flex: 2 ,), ], ), )); } }
# Flutter 流式布局 (Wrap):flutter 为我们提供了 Wrap 这个 widget 来制造弹性布局
使用 有状态的 StatefulWidget 来构建 wrap 布局
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class WrapDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<WrapDemo> createState() => _WrapDemoState(); } class _WrapDemoState extends State <WrapDemo > var list = <int >[]; @override void initState() { super .initState(); for (var i = 0 ; i < 20 ; i++) { list.add(i); } } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Wrap( direction: Axis.horizontal, alignment: WrapAlignment.start, spacing: 1.0 , runSpacing: 1.0 , children: list.map((e) => Container( height: 100 , width: 100 , child: Text( e.toString(), style: TextStyle( color: Colors.black, fontSize: 20 ) ), color: Colors.blue, )).toList() ); } }
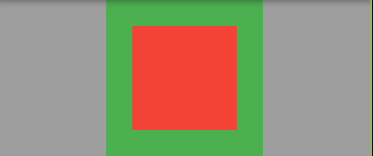
# Flutter 层叠布局 (Stack):flutter 为我们提供了 Stack 这个 widget 来制造层叠布局
我们设置了两个容器 div,在层叠布局中,如果后一个容器,比前面的容器大,那么就会遮挡,原理是为什么?
flutter 在绘画时,从 x 0 y 0 开始绘画,也就是 左上角
意味着两个容器绘画开始的坐标都是相同的,只不过宽高不一样
那么如果第一个容器宽高为 100 第二个为 150 就理所应当的遮住啦!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class StackDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( color: Colors.grey, width: double .infinity, child: Stack( alignment: AlignmentDirectional.center, children: [ Container( color: Colors.green, width: 150 , height: 150 , ), Container( color: Colors.red, width: 100 , height: 100 , ), ], ), ); } }
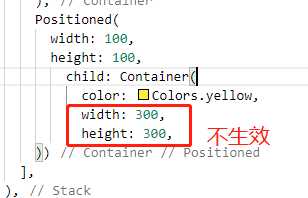
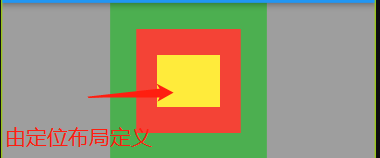
# Flutter 定位布局 (Positioned):flutter 为我们提供了 Positioned 这个 widget 来制造层叠布局
如果 Positioned 设置了宽高,那么子组件不生效
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 top: 10 , bottom: 10 , 那么就不能设置高度 height left: 10 , right: 10 , 那么就不能设置宽度 width
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class StackDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( color: Colors.grey, width: double .infinity, child: Stack( alignment: AlignmentDirectional.center, children: [ Container( color: Colors.green, width: 150 , height: 150 , ), Container( color: Colors.red, width: 100 , height: 100 , ), Positioned( child: Container( color: Colors.yellow, width: 300 , height: 300 , ), top: 50 , left: 150 , right: 150 , bottom: 50 , ) ], ), ); } }
# Flutter 相对定位 (Align):flutter 为我们提供了 Align 这个 widget 来制造层叠布局
要点:只会相对于父组件来定位,而不是屏幕
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class AlignDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( width: 200 , height: 200 , color: Colors.green, child: Align( alignment: Alignment.center, child: FlutterLogo( size: 60 , ), ), ); } }
# Flutter 的内外边距 Padding、Marginflutter 为我们提供了 padding 和 margin 这量个 属性来设置内外边距
内边距:当前容器内的组件对于当前容器的距离
外边距:当前容器距离父类容器的距离
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class PaddingAndMarginDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( width: 100 , height: 100 , color: Colors.red, margin: EdgeInsets.all(10 ), padding: EdgeInsets.all(20 ), child: Text("我有边距" ), ); } }
要点:子 widget 没有设置宽高的时候取自己设置的最大宽高
ConstrainedBox 的特点就是可以设置最大或者最小的宽高,子组件怎么设置都不可以超过这个宽高
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class ConstrainedBoxDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return ConstrainedBox( constraints: BoxConstraints( maxHeight: 100 , maxWidth: 100 , minHeight: 50 , minWidth: 50 , ), child: Container( width: 500 , height: 500 , color: Colors.red, ), ); } }
要点:如果父容器指定了宽高,那么子组件不可以修改宽高
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class ConstrainedBoxDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return SizedBox( child: Container( color: Colors.red, width: 200 , height: 200 , ), ); } }
flutter 为我们提供了 BoxDecoration 这量个 widget 来设置样式装饰
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class ConstrainedBoxDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( margin: EdgeInsets.all(20 ), width: double .infinity, child: DecoratedBox( decoration: BoxDecoration( gradient: LinearGradient( colors: [ Colors.red, Colors.green, ], ), borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0 ), boxShadow: [ BoxShadow( color: Colors.black, offset: Offset(2.0 ,2.0 ), blurRadius: 2 , ) ], ), child: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.only( left: 100 , right: 100 , top: 20 , bottom: 20 ), child: Text( "渐变色~" , style: TextStyle( color: Colors.white ), textAlign: TextAlign.center, ), ), ), ); } }
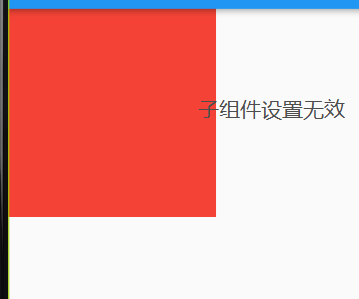
要点:当 Container 设置了 foregroundDecoration(前景) 的背景颜色,那么子组件将不会显示
要点:当 Container 设置了 decoration(背景) 的背景颜色,那么子组件将会显示
设置内边距并旋转 0.5
代码演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class ContarinerDemo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Container( margin: EdgeInsets.all(100 ), width: 100 , height: 100 , child: Text("data" ), decoration: BoxDecoration( color: Colors.red ), transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.5 ), ); } }
1.MateriaApp 是 flutter 的根节点,flutter 规定必须要 MateriaApp 来作为根节点展示
2. 在 MateriaApp 可以设置路由,每个子页面必须由 Scaffold 来包裹
3. 每个 Scaffold 包含两个部分 appBar(头部),body(展示体)
# Flutter 的 AppBar:Scaffold 中的 AppBar 有很多特性:
代码演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class PageDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<PageDemo> createState() => _PageDemoState(); } class _PageDemoState extends State <PageDemo > @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( leading: IconButton( onPressed: () { print ("点击了!" ); }, icon: Icon(Icons.home) ), title: Text( "演示" , style: TextStyle(fontSize: 15 ), ), actions: [ IconButton( onPressed: () { print ("点击了加!" ); }, icon: Icon(Icons.add)), IconButton( onPressed: () { print ("点击了减!" ); }, icon: Icon(Icons.remove)), IconButton( onPressed: () { print ("点击了灯!" ); }, icon: Icon(Icons.wb_iridescent_rounded)), ], elevation: 10.0 , ), ); } }
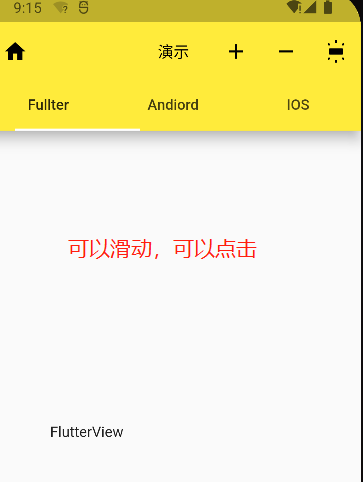
# Flutter 的顶部 TabBar 选项卡:Flutter 提供 顶部 TabBar 选项卡
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class PageDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<PageDemo> createState() => _PageDemoState(); } class _PageDemoState extends State <PageDemo > with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin List tabs = ["Fullter" , "Andiord" , "IOS" ]; late TabController _controller = TabController(length: tabs.length, vsync: this ); int _index = 0 ; @override void initState() { _controller = TabController( initialIndex: _index, length: tabs.length, vsync: this ); _controller.addListener(() { setState(() { _index = _controller.index; }); }); super .initState(); } @override void dispose() { _controller.dispose(); super .dispose(); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( elevation: 10.0 , bottom: TabBar( controller: _controller, tabs: tabs.map((e) => Tab( text: e, )).toList(), ), ), body: Text(_index.toString()), ); } }
# Flutter 的顶部 TabBar 选项卡(进阶)使用 Flutter 提供 顶部 TabBarView 组件来设置选项卡
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class PageDemo extends StatefulWidget List <Widget> widgets = [FlutterView(),AndroidView(),IOSView()]; @override State<PageDemo> createState() => _PageDemoState(); } class _PageDemoState extends State <PageDemo > with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin List tabs = ["Fullter" , "Andiord" , "IOS" ]; late TabController _controller = TabController(length: tabs.length, vsync: this ); @override void initState() { _controller = TabController( length: tabs.length, vsync: this ); super .initState(); } @override void dispose() { _controller.dispose(); super .dispose(); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( elevation: 10.0 , bottom: TabBar( controller: _controller, tabs: tabs.map((e) => Tab( text: e, )).toList(), ), ), body: TabBarView( children: widget.widgets, controller: _controller, ) ); } } class FlutterView extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Center( child: Text("FlutterView" ), ); } } class AndroidView extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Center( child: Text("AndroidView" ), ); } } class IOSView extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Center( child: Text("IOSView" ), ); } }
# Flutter 的侧抽屉 Drawer 样式使用 Flutter 提供 侧抽屉 Drawer 组件来设置抽屉样式
# 要点:drawer 是 Scaffold 中的属性,并不是 AppBar 的
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class myDrawer extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Drawer( child: MediaQuery.removePadding( context: context, child: Column( crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start, children: [ Padding(padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 40 ), child: Text("Brath" ), ) ], ), removeTop: true , ), ); } }
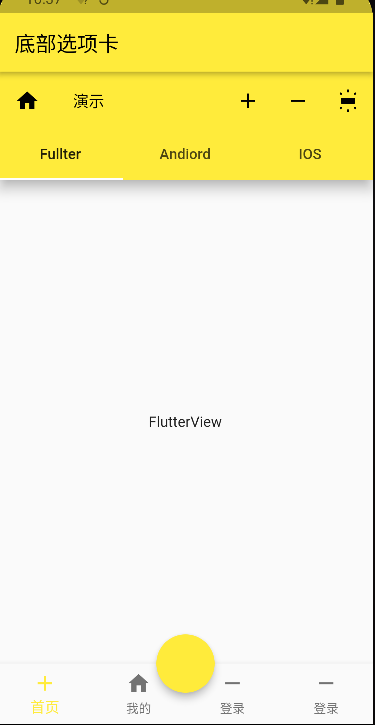
# Flutter 的底部选项卡使用 flutter 提供的 bottomNavigationBar 来做底部选项卡,做到点击卡片切换页面
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class BottomNavigatorBarDemo extends StatefulWidget const BottomNavigatorBarDemo({ Key? key }) : super (key: key); @override State<BottomNavigatorBarDemo> createState() => _BottomNavigatorBarDemoState(); } class _BottomNavigatorBarDemoState extends State <BottomNavigatorBarDemo > int _index = 0 ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("底部选项卡" ), ), bottomNavigationBar: BottomNavigationBar( items: [ BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.add), label: "新增" ), BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.home), label: "我的" ), BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.remove), label: "减少" ), ], currentIndex: _index, onTap: (v){ setState(() { _index = v; }); }, ), body: Center(child: Text(_index.toString())), ); } }
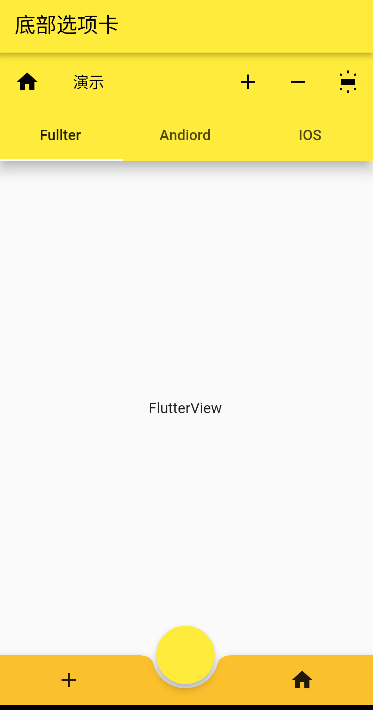
# Flutter 的底部选项卡(进阶版)使用 flutter 提供的 bottomNavigationBar 来做底部选项卡,做到按钮居中布局
要点:两种实现方式,BottomNavigationBar 中如果 BottomNavigationBarItem 超过三个需要设置 type👇否则不显示
1 type: BottomNavigationBarType.fixed
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class BottomNavigatorBarDemo extends StatefulWidget List <Widget> widgets = [ PageDemo(), LayoutDemo(), LoginPage(), LoginPage(), ]; @override State<BottomNavigatorBarDemo> createState() => _BottomNavigatorBarDemoState(); } class _BottomNavigatorBarDemoState extends State <BottomNavigatorBarDemo > int _index = 0 ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("底部选项卡" ), ), bottomNavigationBar: BottomNavigationBar( type: BottomNavigationBarType.fixed, items: [ BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.add), label: "首页" ), BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.home), label: "我的" ), BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.remove), label: "登录" ), BottomNavigationBarItem( icon: Icon(Icons.remove), label: "登录" ), ], currentIndex: _index, onTap: (v){ setState(() { _index = v; }); }, ), floatingActionButtonLocation: FloatingActionButtonLocation.centerDocked, floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( onPressed: (){ print ("object" ); }, ), body: widget.widgets[_index], ); } }
第二种实现方式:
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class _BottomNavigatorBarDemoState extends State <BottomNavigatorBarDemo > int _index = 0 ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("底部选项卡" ), ), bottomNavigationBar: BottomAppBar( color: Theme.of(context).primaryColorDark, shape: CircularNotchedRectangle(), child: Row( mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceAround, children: [ IconButton( onPressed: (){ }, icon: Icon(Icons.add)), SizedBox(height: 16 ), IconButton( onPressed: (){ }, icon: Icon(Icons.home)), ] ), ), floatingActionButtonLocation: FloatingActionButtonLocation.centerDocked, floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( onPressed: (){ print ("object" ); }, ), body: widget.widgets[_index], ); } }
flutter 为我们提供了 ListView 这个 widget 来展示我们的列表
源码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 ListView({ Key? key, Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical, bool reverse = false , ScrollController? controller, bool? primary, ScrollPhysics? physics, bool shrinkWrap = false , EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding, this .itemExtent, this .prototypeItem, bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true , bool addRepaintBoundaries = true , bool addSemanticIndexes = true , double? cacheExtent, List <Widget> children = const <Widget>[], int? semanticChildCount, DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start, ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual, String? restorationId, Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge, })
# 用 ListView 实现滑动列表,并且可以细粒度显示每个 list 数据,并且可以点击按钮返回顶部
代码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class ListViewDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<ListViewDemo> createState() => _ListViewDemoState(); } class _ListViewDemoState extends State <ListViewDemo > List <int > list = []; ScrollController _controller = ScrollController(); bool show = false ; @override void initState() { super .initState(); _controller = ScrollController(); _controller.addListener(() { if (_controller.offset >= 100 && show == false ){ setState(() { show = true ; }); }else if (_controller.offset < 100 && show == true ){ setState(() { show = false ; }); } }); for (var i = 0 ; i < 100 ; i++) { list.add(i); } } @override void dispose() { super .dispose(); _controller.dispose(); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("滚动列表" ), ), floatingActionButton: show ? FloatingActionButton( child: Icon(Icons.vertical_align_top_outlined), onPressed: (){ _controller.animateTo( 0 , duration: Duration (milliseconds: 300 ), curve: Curves.slowMiddle ); }, ): null , body: Scrollbar( child: RefreshIndicator( child: ListView.builder( itemBuilder: (BuildContext context,int index){ if (index == 2 ){ return Icon(Icons.add); } return Text(list[index].toString()); }, itemCount: list.length, controller: _controller, ), onRefresh: _onRefresh, ) ) ); } Future _onRefresh() async { await Future.delayed( Duration (seconds: 3 ), (){ print ("三" ); } ); return "三" ; } }
flutter 为我们提供了 GridView 这个 widget 来展示我们的网格数据
源码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 GridView({ Key? key, Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical, bool reverse = false , ScrollController? controller, bool? primary, ScrollPhysics? physics, bool shrinkWrap = false , EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding, required this .gridDelegate, bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true , bool addRepaintBoundaries = true , bool addSemanticIndexes = true , double? cacheExtent, List <Widget> children = const <Widget>[], int? semanticChildCount, DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start, Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge, ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual, String? restorationId, })
代码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Grid_view_demo extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("网格布局演示" ), ), body: GridView( gridDelegate: SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount( crossAxisCount: 2 , mainAxisSpacing: 10 , crossAxisSpacing: 10 , ), children: [ Container( color: Colors.amber, ), Container( color: Color.fromARGB(255 , 85 , 76 , 51 ), ), Container( color: Color.fromARGB(255 , 14 , 223 , 125 ), ), Container( color: Color.fromARGB(255 , 42 , 45 , 209 ), ), ], ), ); } }
flutter 为我们提供了 AlertDialog 这个 widget 来展示我们的弹窗数据
源码阅读:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 const AlertDialog({ Key? key, this .title, this .titlePadding, this .titleTextStyle, this .content, this .contentPadding = const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(24.0 , 20.0 , 24.0 , 24.0 ), this .contentTextStyle, this .actions, this .actionsPadding = EdgeInsets.zero, this .actionsAlignment, this .actionsOverflowDirection, this .actionsOverflowButtonSpacing, this .buttonPadding, this .backgroundColor, this .elevation, this .semanticLabel, this .insetPadding = _defaultInsetPadding, this .clipBehavior = Clip.none, this .shape, this .alignment, this .scrollable = false , })
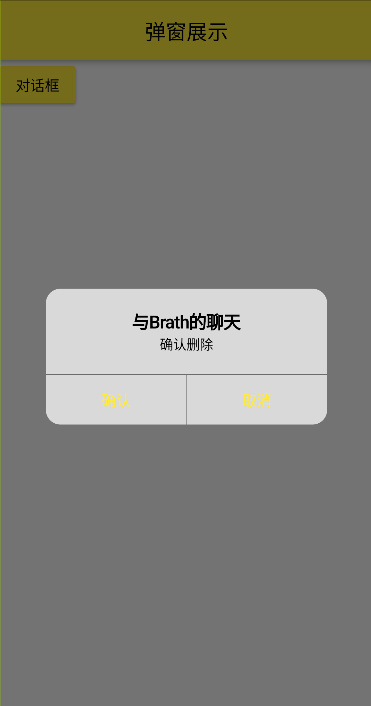
# 图片为 IOS 风格的弹窗
代码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class AlertDialogDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<AlertDialogDemo> createState() => _AlertDialogDemoState(); } class _AlertDialogDemoState extends State <AlertDialogDemo > @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("弹窗展示" ), ), body: Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: _showAlert, child: Text("对话框" )) ], ), ); } void _showAlert() async { var res = await showDialog( context: context, builder: (BuildContext context) { return CupertinoAlertDialog( title: Text("与Brath的聊天" ), content: Text("确认删除" ), actions: [ TextButton(onPressed: () { Navigator.of(context).pop(true ); }, child: Text("确认" )), TextButton(onPressed: () { Navigator.pop(context,false ); }, child: Text("取消" )), ], ); }, ); print (res); } }
flutter 为我们提供了 SimpleDialog 这个 widget 来展示我们的弹框数据
源码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const SimpleDialog({ Key? key, this .title, this .titlePadding = const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(24.0 , 24.0 , 24.0 , 0.0 ), this .titleTextStyle, this .children, this .contentPadding = const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(0.0 , 12.0 , 0.0 , 16.0 ), this .backgroundColor, this .elevation, this .semanticLabel, this .insetPadding = _defaultInsetPadding, this .clipBehavior = Clip.none, this .shape, this .alignment, })
代码演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class AlertDialogDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<AlertDialogDemo> createState() => _AlertDialogDemoState(); } class _AlertDialogDemoState extends State <AlertDialogDemo > List <int > list = []; @override void initState() { super .initState(); for (var i = 0 ; i < 20 ; i++) { list.add(i); } } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("弹窗展示" ), ), body: Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: _showAlert, child: Text("对话框" )), ElevatedButton( onPressed: _showList, child: Text("列表框" )), ], ), ); } void _showList() async { var res = await showDialog( barrierDismissible: false , context: context, builder: (BuildContext context) { return SimpleDialog( title: Text("与Brath的聊天" ), children: list.map((e) => GestureDetector( child: Text(e.toString()), onTap: (){ Navigator.pop(context,e); }, )).toList(), ); }, ); print (res); }
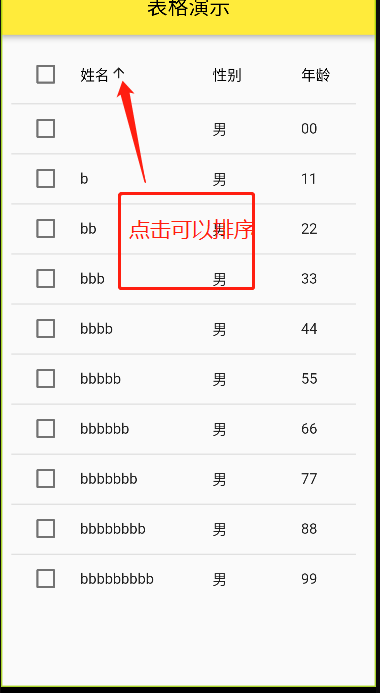
flutter 为我们提供了 Table 还有 DataTable 这两个常用 widget 来展示我们的表格
代码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 class TableDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<TableDemo> createState() => _TableDemoState(); } class _TableDemoState extends State <TableDemo > List <Map > list = []; int _sortColumnIndex = 0 ; bool _sortAscending = true ; @override void initState() { super .initState(); for (var i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { list.add({ "name" : "b" * i, "gender" : i % 1 == 0 ? "男" : "女" , "isSelect" : false , "age" : i.toString() + i.toString(), }); } } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("表格演示" ), ), body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(10 ), child: DataTable( sortColumnIndex: _sortColumnIndex, sortAscending: _sortAscending, columns: [ DataColumn( onSort: (columnIndex, ascending) { setState(() { _sortAscending = ascending; _sortColumnIndex = columnIndex; list.sort((begin,end){ if (!ascending){ var c = begin; begin = end; end = c; } return begin["name" ].toString().length.compareTo(end["name" ].toString().length); }); }); }, label: Text("姓名" ) ), DataColumn( label: Text("性别" ) ), DataColumn( label: Text("年龄" ) ), ], rows: list.map((e) => DataRow( selected: e["isSelect" ], onSelectChanged: (v){ setState(() { if (e["isSelect" ] != v){ e["isSelect" ] = v; } }); }, cells: [ DataCell(Text(e["name" ])), DataCell(Text(e["gender" ])), DataCell(Text(e["age" ])), ] ) ).toList(), ), ) ); } }
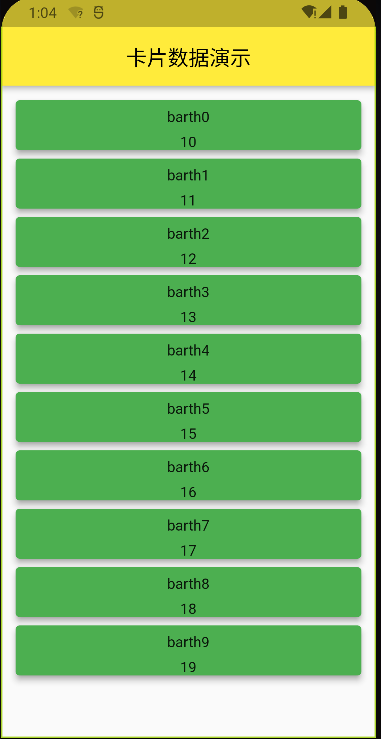
flutter 为我们提供了 Card 这个 widget 来展示我们的卡片数据
代码展示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class CardDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<CardDemo> createState() => _CardDemoState(); } class _CardDemoState extends State <CardDemo > List <Map > list = []; @override void initState() { super .initState(); for (var i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { list.add({ "age" : 10 + i, "name" : "barth" + i.toString(), }); } } Widget _itemBuilder(BuildContext context,int index){ return Card( color: Colors.green, shadowColor: Colors.grey, elevation: 5.0 , child: Column( children: [ SizedBox(height: 8 ), Text(list[index]["name" ]), SizedBox(height: 8 ), Text(list[index]["age" ].toString()), ], ), ); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("卡片数据演示" ), ), body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(10 ), child: ListView.builder( itemBuilder: _itemBuilder, itemCount: list.length, ) ), ); } }
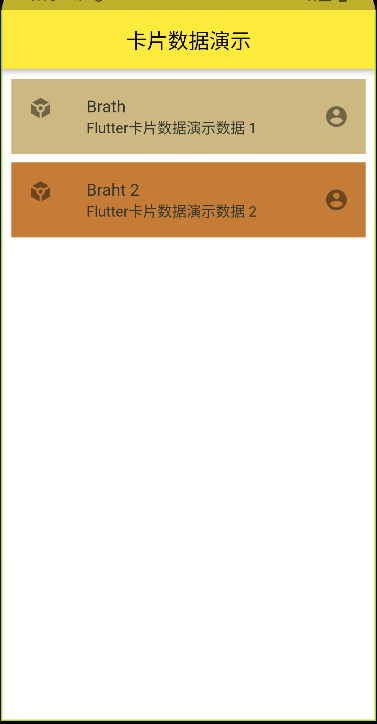
Flutter 为我们提供了 ListTile 这个 Widget 来展示标签
代码演示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( backgroundColor: Colors.white, appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("卡片数据演示" ), ), body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(10 ), child: ListView( children: [ ListTile( tileColor: Color.fromARGB(255 , 204 , 184 , 128 ), leading: Icon(Icons.token_sharp), title: Text("Brath" ), textColor: Color.fromARGB(255 , 49 , 54 , 42 ), subtitle: Text("Flutter卡片数据演示数据 1 " ), trailing: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded), ), SizedBox(height: 8 ), ListTile( tileColor: Color.fromARGB(255 , 197 , 124 , 55 ), leading: Icon(Icons.token_sharp), title: Text("Braht 2" ), textColor: Color.fromARGB(255 , 49 , 54 , 42 ), subtitle: Text("Flutter卡片数据演示数据 2 " ), trailing: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded), ), ], ), ), ); }
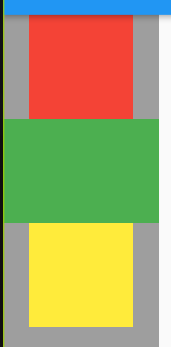
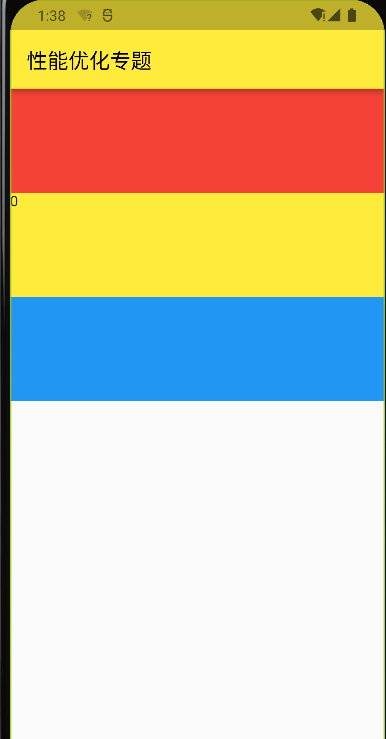
# Flutter 性能优化:先看图片:
我们以看到,这张图片由三个容器构成,并且点击黄色容器,其数字会增加,理论上来说代码并没有任何问题。
但是,在我们打开 检测工具后,发现,当点击黄色容器时,所有容器都会重新渲染,这就造成了性能的损耗!
如何优化?
代码演示:
# 使用一个单独的 CountDemo 来对 黄色的容器进行封装,这样就可以做到单独渲染# 因为 setState 会重新绘制当前组件(Column),单独封装后,他自己就是一个单独组件(CountDemo)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class performanceDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<performanceDemo> createState() => _performanceDemoState(); } class _performanceDemoState extends State <performanceDemo > int count = 0 ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("性能优化专题" ), ), body: Column( children: [ Container( width: double .infinity, height: 100 , color: Colors.red, ), Container( width: double .infinity, height: 100 , color: Colors.yellow, child: CountDemo(), ), Container( width: double .infinity, height: 100 , color: Colors.blue, ) ], ), ); } } class CountDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<CountDemo> createState() => _CountDemoState(); } class _CountDemoState extends State <CountDemo > int count = 0 ; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return GestureDetector( child: Text(count.toString()), onTap: (){ setState(() { count ++; }); }, ); } }
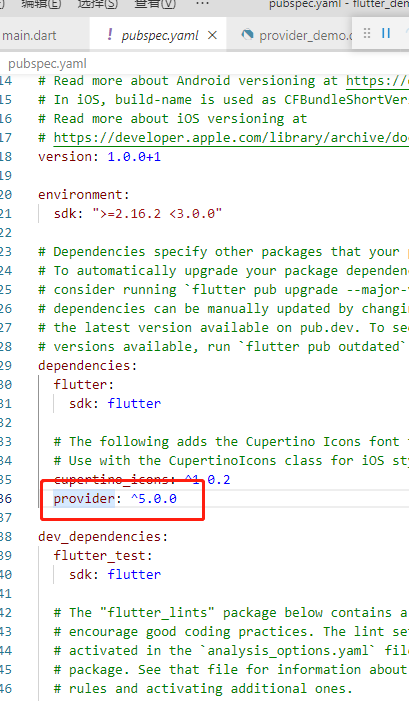
# Flutter 的全局状态管理 Provider 非常重要!# 我们分为四个步骤来学习全局状态管理 Provider# 1、因为全局状态管理是单独的插件,所以我们第一步一定是导包选择根目录下的 pubspec.yaml 依赖配置文件
以作者 Brath 的 flutter 版本 2.0 为例,使用 5.0.0 版本
# 2、下载好依赖后,我们在 lib 目录创建文件夹:Provider 并在文件夹内创建一个 Count_provider.dart,作为我们的第一个全局状态类
在类中写入代码:
# 要点:notifyListeners () 这个方法的作用就是实现局部刷新1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class CountProvider extends ChangeNotifier int _count = 0 ; get count => _count; void add(){ _count ++; notifyListeners(); } }
# 3、我们写一个新的类用于测试全局状态数据 要点:
1. 获取全局变量:
# 通过 Provider 的 of 方法(泛型我们的全局状态类)传入上下文对象,就可以获取 count1 Provider.of<CountProvider>(context).count.toString()
2. 修改全局变量:
# 通过上下文对象的 read 方法(泛型我们的全局状态类),就可以获取状态类中的方法,来操作# Tips:不是从当前页使用方法修改全局变量,而是全局变量提供了方法供外部修改!1 context.read<CountProvider>().add();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class ProviderDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<ProviderDemo> createState() => _ProviderDemoState(); } class _ProviderDemoState extends State <ProviderDemo > @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("Provider全局状态管理" ), ), body: Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: (){ Navigator.of(context).pushNamed("ProviderDemo2" ); }, child: Icon(Icons.add_task_rounded)), Text( Provider.of<CountProvider>(context).count.toString() ) ], ), floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( child: Icon(Icons.sanitizer_sharp), onPressed: (){ context.read<CountProvider>().add(); }, ), ); } } class ProviderDemo2 extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("Provider2" ), ), body: FloatingActionButton( child: Icon(Icons.sanitizer_sharp), onPressed: (){ context.read<CountProvider>().add(); }, ), ); } }
4、在 main.dart 中修改启动方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 main() { runApp( MultiProvider( providers: [ ChangeNotifierProvider( create: (context) => CountProvider(), ), ], child: MyApp(), )); }
# Flutter 的网络请求(DIO)# Flutter 在 pub.dev 为我们提供了许多网络请求组件,我们选择用 DIO 来做请求组件使用方法:
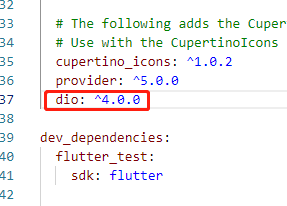
# 1、因为网络请求是单独的插件,所以我们第一步一定是导包选择根目录下的 pubspec.yaml 依赖配置文件
以作者 Brath 的 flutter 版本 2.0 为例,使用 4.0.0 版本
# 2、编写代码:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class DioDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<DioDemo> createState() => _DioDemoState(); } class _DioDemoState extends State <DioDemo > Dio _dio = Dio(); @override void initState() { super .initState(); _dio.options.baseUrl = "https://www.XXX.XXX:0000/" ; } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("网络请求演示" ), ), body: Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: _get , child: Text("getUserinfo" ) ), ] ), ); } void _get () async { var res2 = await _dio.get ( "get/getData" , queryParameters: { "id" : 1 }, options: Options( headers: { "token" : "header-Token" } ) ); print (res2.toString()); } }
# 1. 请求本地连接,ip 地址错误# 2. 未添加网络请求权限# 3. 请求的地址是 http,不是 https# 4. 与服务端的请求参数不同,导致无法请求到接口# Flutter 的设计模式(MVVM)(Model View ViewModel)# MVVM 就是 Model View ViewModel 的简写。# Model :处理接口请求数据# View :展示页面# ViewModel:处理业务逻辑(相当于 Model、View 的链接层)# 简单流程:view 通知 viewModel 层,viewModel 通知 Model 层调用接口,viewModel 层接收 Model 的数据,响应给 view 层展示# 我们通过几个步骤来演示 MVVM 模式的请求流程,以及他的优缺点# 1、首先创建 Model View ViewModel 三个文件夹# 2、编写 Model 层 (请求数据)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class MvvmModel dynamic get (int id) async { print ("开始调用userinfo接口" ); var res = await Dio().get ( "https://xxx:0000/gerUserInfo" , queryParameters: { "userId" : id }, ); print ("调用完毕" ); return res; } }
# 3、编写 View 层 (接收、展示数据)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class MvvmViewDemo extends StatefulWidget @override State<MvvmViewDemo> createState() => _MvvmViewDemoState(); } class _MvvmViewDemoState extends State <MvvmViewDemo > dynamic res; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( centerTitle: true , title: Text("View展示页面" ), ), body: Column( children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: () async { context.read<MvvmViewModel>().get (1 ); }, child: Text("调用ViewwModel获取用户userinfo" ) ), ], ), ); } }
# 4、编写 ViewModel 层 (整合 view 以及 model:view 调用 ViewModel ,ViewModel 调用 model 返回结果给 view)tips:在调用完接口后跳转时,因为 Navigator 需要一个上下文对象,但是我们当前没有上下文对象,所以要在 main 入口定义一个对象:
main.dart👇
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 final GlobalKey<NavigatorState> navigatorkey = GlobalKey<NavigatorState>();class MyApp extends StatelessWidget @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( navigatorKey: navigatorkey, ); } }
MvvmViewModel.dart👇
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class MvvmViewModel extends ChangeNotifier MvvmModel _model = MvvmModel(); void get (int id) async { Response res = await _model.get (id); print (res.data); print (res.headers); print (res.statusCode); print (res.realUri); Navigator.of(navigatorkey.currentContext!).pushNamed("DioDemo" ); } }
# 5、DIO 返回值 Response 介绍1 2 3 4 5 Response res = await _model.get (id); print (res.data); print (res.headers); print (res.statusCode); print (res.realUri);
本篇至此就结束啦!如果你读到了这里,不妨给我点个赞,我叫 Brath,是一个非科班出身的技术狂!
我的博客 brath.top 欢迎访问!
# 关于我Brath 是一个热爱技术的 Java 程序猿,公众号「InterviewCoder」定期分享有趣有料的精品原创文章!
非常感谢各位人才能看到这里,原创不易,文章如果有帮助可以关注、点赞、分享或评论,这都是对我的莫大支持!